Self-Service Business Intelligence Software: A Powerful Tool for Risk Management
In today’s data-driven world, businesses are constantly seeking ways to gain a competitive edge. One of the most effective tools for achieving this is self-service business intelligence software. This software empowers users to analyze data, generate insights, and make informed decisions. However, its capabilities extend far beyond simple data visualization. A key area where this software truly shines is in identifying and highlighting potential risks, enabling proactive mitigation strategies.
This article delves into the capabilities of self-service business intelligence software, focusing on how it can be leveraged to identify, assess, and manage risks effectively. We will explore various use cases, benefits, and best practices for implementing this powerful technology.
Understanding Self-Service Business Intelligence
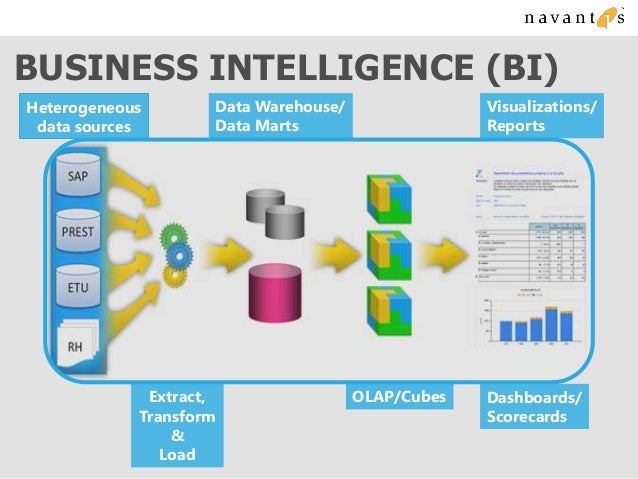
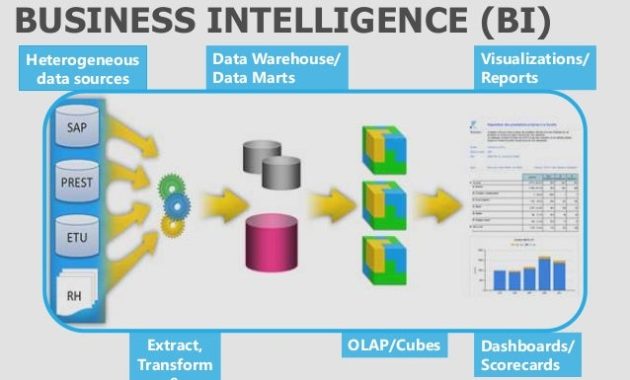
Self-service business intelligence (BI) refers to the ability of business users, not just IT professionals or data scientists, to access, analyze, and visualize data without relying heavily on technical assistance. This democratization of data empowers employees across all departments to make data-driven decisions. The software typically offers user-friendly interfaces, drag-and-drop functionalities, and pre-built dashboards, making data exploration accessible to a wider audience.
Key features often include:
- Data integration from various sources (databases, spreadsheets, cloud services).
- Interactive dashboards and visualizations (charts, graphs, maps).
- Ad-hoc reporting and data exploration capabilities.
- Data modeling and transformation tools.
- Collaboration and sharing features.
The core value proposition of self-service BI lies in its ability to provide timely and relevant insights. This allows businesses to respond quickly to changing market conditions, identify opportunities, and, crucially, mitigate potential risks.
How Self-Service Business Intelligence Highlights Risks
Self-service business intelligence software is not just about creating pretty charts. It’s a powerful tool for identifying and analyzing potential risks across various business functions. The software can automate the process of identifying anomalies, trends, and patterns that might indicate potential problems. It can also be used to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and set up alerts for when these indicators fall outside of predefined thresholds.
Here are some specific ways self-service BI can highlight risks:
- Financial Risk: Monitoring cash flow, identifying potential fraud, tracking revenue trends, and analyzing customer payment patterns.
- Operational Risk: Tracking production efficiency, identifying bottlenecks in processes, monitoring supply chain performance, and analyzing customer service metrics.
- Compliance Risk: Monitoring adherence to regulatory requirements, tracking data privacy compliance, and identifying potential legal issues.
- Market Risk: Analyzing competitor activity, monitoring market trends, and identifying changes in customer behavior.
- IT Risk: Monitoring system performance, identifying security vulnerabilities, and tracking data breaches.
By providing real-time insights into these areas, self-service business intelligence allows businesses to proactively address potential problems before they escalate into major crises.
Use Cases: Real-World Examples of Risk Mitigation
The application of self-service business intelligence software in risk management is broad. Several real-world examples highlight its effectiveness:
- Retail: A retail chain uses self-service BI to analyze sales data and identify products with high return rates. This allows them to investigate the reasons behind the returns (e.g., product defects, poor quality) and take corrective actions. This reduces financial losses and protects the brand reputation.
- Healthcare: A hospital uses self-service BI to monitor patient readmission rates. By analyzing data on patient demographics, treatment plans, and discharge instructions, they can identify factors that contribute to readmissions. This allows them to improve patient care and reduce hospital costs.
- Manufacturing: A manufacturing company uses self-service BI to track equipment performance and identify potential maintenance issues. By analyzing data on machine downtime, energy consumption, and production output, they can predict when equipment failures are likely to occur. This allows them to schedule preventative maintenance and avoid costly production disruptions.
- Financial Services: A bank uses self-service BI to monitor customer transaction data for fraudulent activity. By analyzing patterns in spending, location, and transaction amounts, they can identify suspicious transactions and alert customers to potential fraud. This protects customers and reduces financial losses.
These examples demonstrate the versatility of self-service BI in addressing various types of risks across different industries.
Benefits of Using Self-Service Business Intelligence for Risk Management
Implementing self-service business intelligence software for risk management offers several compelling benefits:
- Proactive Risk Identification: The software allows organizations to proactively identify potential risks before they cause significant damage.
- Improved Decision-Making: Data-driven insights empower stakeholders to make better-informed decisions about risk mitigation strategies.
- Increased Efficiency: Automation of data analysis and reporting saves time and resources, allowing risk managers to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Enhanced Collaboration: The software facilitates collaboration between different departments, improving communication and coordination in risk management efforts.
- Reduced Costs: By identifying and mitigating risks early, organizations can avoid costly losses and improve operational efficiency.
- Better Compliance: Self-service BI helps organizations monitor and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements.
The advantages are clear: self-service business intelligence is an investment in a more resilient and data-driven future.
Best Practices for Implementing Self-Service Business Intelligence
Successful implementation of self-service business intelligence software requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices to consider:
- Define Clear Objectives: Establish specific goals for using the software, such as reducing fraud, improving operational efficiency, or enhancing compliance.
- Choose the Right Software: Select a self-service BI platform that meets your specific needs and budget. Consider factors such as ease of use, data integration capabilities, and analytical features.
- Ensure Data Quality: Implement data governance policies and procedures to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of your data.
- Provide Training and Support: Train users on how to use the software effectively and provide ongoing support to address any questions or issues.
- Foster a Data-Driven Culture: Encourage a culture of data-driven decision-making throughout the organization.
- Establish a Risk Management Framework: Integrate the use of self-service BI into your existing risk management framework to ensure a holistic approach.
- Monitor and Evaluate Results: Regularly monitor the performance of the software and evaluate its effectiveness in mitigating risks.
By following these best practices, organizations can maximize the value of their self-service BI investment and achieve their risk management objectives.
The Future of Self-Service Business Intelligence in Risk Management
The role of self-service business intelligence software in risk management is poised to grow. Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are further enhancing the capabilities of these tools. AI-powered BI platforms can automate complex analyses, identify hidden patterns, and provide predictive insights. This will enable businesses to anticipate risks with greater accuracy and develop more effective mitigation strategies.
Furthermore, the increasing complexity of data and the evolving regulatory landscape will continue to drive the adoption of self-service BI. Organizations will need powerful and flexible tools to manage their data effectively and ensure compliance.
The future is bright for self-service business intelligence, particularly in the realm of risk management. It is becoming an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to thrive in an increasingly uncertain and competitive environment. [See also: The Role of Data Governance in Risk Mitigation] and [See also: Choosing the Right BI Tool for Your Business].
Conclusion
Self-service business intelligence software is a transformative technology that empowers organizations to identify, assess, and manage risks effectively. By providing timely insights, automating data analysis, and facilitating collaboration, this software enables businesses to make data-driven decisions and proactively mitigate potential problems. As the business landscape becomes more complex and data-driven, the adoption of self-service business intelligence will continue to grow, making it an essential tool for any organization seeking to protect its interests and achieve its strategic objectives.